Lab 7 - Recursion exercises
On competing the lab you will:
- Implement recursive algorithms.
Recursive Exercises
Create a new project in Eclipse called Lab7Recursion.
Binary Number. Write a recursive algorithm for finding the binary representation of a decimal number. (hint: repeatedly divide 2 into the decimal number and read the remainders backwards) .Provide a Java implementation, BinaryNumbers.java, and ascertain the growth order.
Reversing a String. Write two methods, one non-recursive and one recursive, that returns a String that is the reverse of the input String.e.g. System.out.println(reverseString(“Darragh and Ronan”)); would print: “nanoR dna hgarraD”.
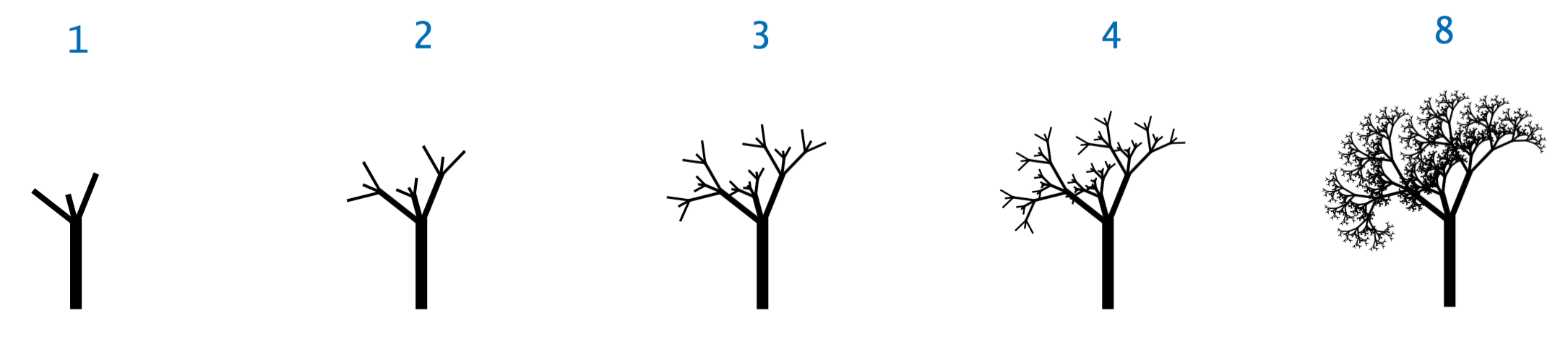
A Tree. Create and run the following fractal program that draws a tree. You will need to put stdlib_package.jar on your build path. Modify the program such that it includes a four branches(e.g. include a forth recursive call).
import edu.princeton.cs.introcs.StdDraw;
public class TreeFractal{
public static void tree(int n, double x, double y, double a, double branchRadius) {
double bendAngle = Math.toRadians(15);
double branchAngle = Math.toRadians(37);
double branchRatio = 0.65;
double cx = x + Math.cos(a) * branchRadius;
double cy = y + Math.sin(a) * branchRadius;
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.001 * Math.pow(n, 1.2));
StdDraw.line(x, y, cx, cy);
if (n == 0) return;
tree(n-1, cx, cy, a + bendAngle - branchAngle, branchRadius * branchRatio);
tree(n-1, cx, cy, a + bendAngle + branchAngle, branchRadius * branchRatio);
tree(n-1, cx, cy, a + bendAngle, branchRadius * (1 - branchRatio));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
StdDraw.enableDoubleBuffering();
tree(n, 0.5, 0, Math.PI/2, 0.3);
StdDraw.show();
}
}
- Cubes: Consider the following recursive algorithm for computing the sum of the first n cubes: S(n) = 13 + 23 + ... + n
3
Implement this is Java. How does this algorithm compare with the straightforward non-recursive algorithm for computing this function?Algorithm S(n) //Input: A positive integer n //Output: The sum of the first n cubes if n = 1 return 1 else return S(n − 1) + n ∗ n ∗ n
- Design a recursive algorithm for computing 2n for any non-negative integer n that is based on the formula: 2n = 2(n−1) + 2(n−1). Set up a recurrence relation for the number of additions made by the algorithm and solve it. Is it a good algorithm for solving this problem?
- Consider the following recursive algorithm.
What does this algorithm compute? Set up a recurrence relation for the algorithm’s basic operation count and solve it.Algorithm Min1 (A[0..n − 1]) //Input: An array A[0..n − 1] of real numbers if n = 1 return A[0] else temp ← Min1 (A[0..n − 2]) if temp ≤ A[n − 1] return temp else return A[n − 1]